Waste Not
For our drinking water and communities.
Sustainable Conservation promotes appropriate, scalable solutions to reimagine waste by reusing manure nutrients, connecting farmers and their land to a circular resource economy, reducing groundwater and greenhouse gas pollution, and building soil health.
Nitrate is the most common drinking water pollutant from human activities – primarily from overapplication of manure and synthetic fertilizers on crops vital to California’s agricultural economy and our collective health.
We envision a future in which all dairy manure is put to beneficial use – protecting groundwater quality, reducing greenhouse gases, building soil health, and boosting co-benefits.
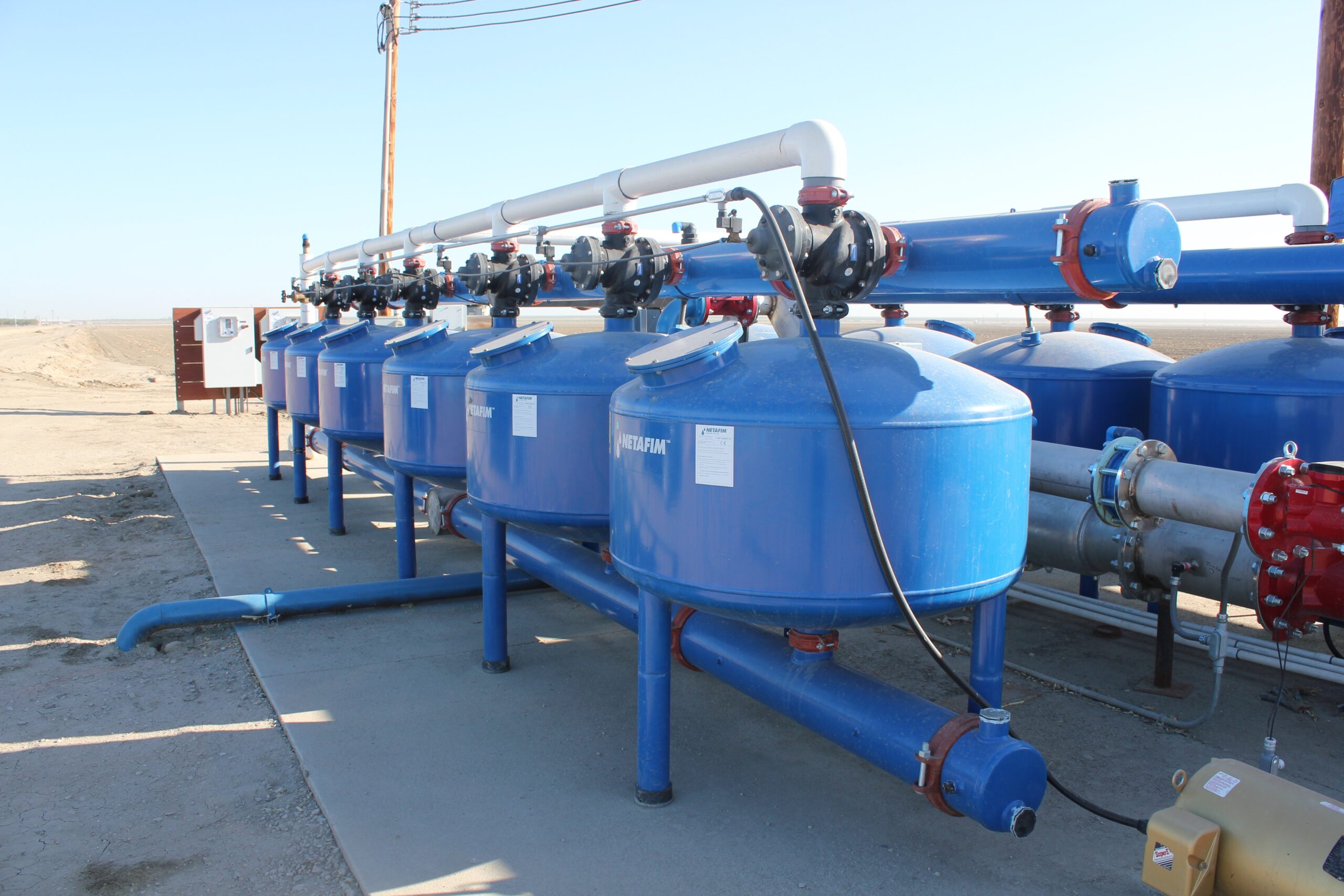
In 2014, Sustainable Conservation teamed up with Netafim USA and a dairy farm to prototype a Manure Subsurface Drip Irrigation (MSDI) system – blending cow manure and water to precisely irrigate and fertilize dairy feed crops. The MSDI innovation allows dairies to be more efficient with water and nutrients and continue using their manure instead of synthetic fertilizers. The system currently irrigates 4,432 acres of feed crop in California — reducing 2.3 billion gallons of applied water, reducing 6.5 million pounds of CO2 equivalents, and preventing 2.4 million pounds of nitrogen loading annually.
Illustration description here, replace this text.
Can Dairies be Environmentally Sustainable?
Watch our panel of experts discuss greenhouse gas emissions, other important environmental considerations, and what California dairies are doing to address these challenges.
Manure Subsurface Drip Irrigation Summary Evaluation
Our project in California demonstrated how manure subsurface drip irrigation (MSDI), an NRCS-approved standard practice, can be modified to apply liquid manure – a natural fertilizer source found on dairies. This new system protects groundwater quality through precision nutrient application, and reduces irrigation-related greenhouse gas emissions.
Read the EvaluationFoundations for Scaling Up
- Growing MSDI’s feed crop footprint and validating its GHG benefits
- Removing the barriers to manure compost
- Demonstrating safe MSDI use with human-consumed crops
- Researching the benefits of incorporating manure into whole orchard recycling
Related resources
See updates and media coverage about this project; the list of organizations partnering with us on this work; and reports and publications relevant to the beneficial use of farm and dairy waste.
- Valley Ag Voice
Central Valley Farms Lead the Way in Water-Saving Irrigation - AgAlert
Climate-smart practices help dairies, nourish crops - CalMatters
After the deluge: Floods may taint more drinking water in California - Business Wire
Netafim USA Spotlights Global Sustainability at 2023 World Ag Expo; Award-winning SDI-E System Is Proven to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions by up to 90%
- BEAM Circular
- CalCAN
- California Air Resources Board
- California Dairy Campaign
- California Dairy Quality Assurance Program
- California Department of Food and Agriculture
- California Natural Resources Conservation Service
- California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo
- California State Water Resources Control Board
- City of Modesto
- Community Alliance with Family Farmers
- Community Water Center
- Dairy Cares
- Dairy Management Inc.
- De Jager Farms
- Governor’s Office of Business and Economic Development
- Leadership Counsel for Justice and Accountability
- Nestle
- Netafim USA
- Newtrient, LLC
- Regional Water Quality Control Boards
- San Joaquin Valley Air Pollution Control District
- Stanislaus Community Foundation
- Stanislaus County
- Starbucks
- Turlock Irrigation District
- UC Davis
- UC Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources
- University of California Cooperative Extension
- Western United Dairies
Water Quality
Resources for farmers, industry and stakeholders to reduce water quality impacts from manure management.
- Subsurface Drip Irrigation System Overview
- Manure Subsurface Drip Irrigation Summary Evaluation
- Considerations for Switching From Flood to Manure Subsurface Drip Irrigation for Forage Production
- Cost Analysis of Manure Subsurface Drip System on California Dairies
- Evaluation of the Agronomic and Environmental Impacts of Manure Subsurface Drip Systems
- Nutrient and Salinity Management Guidance for Manure Subsurface Drip Systems
- NRCS Environmental Quality Incentives Program
- Dairy Conservation Navigator: MSDI
- Nutrient Management Field Guide
Greenhouse Gas Reductions
Resources for farmers, industry and stakeholders to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in California’s dairy industry
CAPCOA GHG Rx
Registry and exchange for California greenhouse gas emissions reductions credits
Reports
- Biomethane from Dairy Waste: A Sourcebook for the Production and Use of Renewable Natural Gas in California: Report on the feasibility of producing biomethane from dairy manure, including technologies, applications and markets for products
- Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Strategies for CA Dairies: Report examining strategies for CARB in developing a short-lived climate pollutants (SLCP) emissions-reduction plan that includes reducing methane emissions from dairies (Read Summary here)
- Compost: Enhancing the Value of Manure (Full Report): Report that examines the barriers to and mechanisms for creating a market for dairy manure compost (Read Executive Summary here)
- Nitrous oxide emissions in subsurface drip and flood irrigated dairy forage production systems: Study of the impact on nitrous oxide emissions from switching from flood irrigation to drip irrigation using manure (Poster)
- Cost-effective and Environmentally Beneficial Dairy Manure Management Practices: Report examining potential dairy manure management practices, economic impacts and environmental benefits
- An Assessment of Technologies for Management and Treatment of Dairy Manure in California’s San Joaquin Valley: Report examining dairy manure management technologies, their feasibility and further research needed




